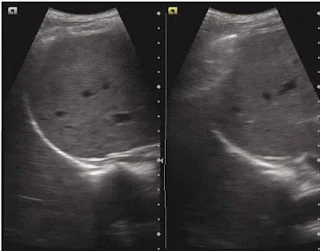
- Curtain sign is a sonographic characteristics of the inferior most part of the lateral lung which occupies the costophrenic recess.
- Curtain sign in normal lung will demonstrate
- Dynamic movement of the lung curtain which is due to expansion and retraction of the lung (Lung curtain moves up and down).
- Lateral aspect of the diaphragm and the upper abdomen is always covered/obscured by the lung curtain, irrespective of the phase of the respiratory cycle.
- Absence of either or of the above results in curtain sign which is commonly seen in pleural effusion.
Curtain sign – the aerated lung in the costophrenic recess overlaps part of liver and diaphragm creating a demarcated leading edge of the lung air artefact, giving the appearance of curtain (of air). Both images are in different part of the respiratory cycle
Click here for the video : Curtain Sign / Abnormal Curtain Sign
Quad sign
In case of pleural effusion, the pleural layers are separated by fluid in between, the visceral pleura appears as a line (the lung line), which is regular and almost parallel to the parietal pleura (pleural line). Together with shadows from the adjacent rins, these lines draw a four sided figure which is known as the Quad sign .
Sinusoid sign
When examined on the M-Mode, a sinusoid pattern is seen which is due to the movement of the lung line towards the pleural line on inspiration and back on expiration. This is called as a sinusoid sign.
A. quad sign: The area of pleural effusion is framed within four regular borders: the pleural line-P, the shadow of the ribs (stars), and the almost regular deep border, which is the lung line-L; B Sinusoid sign : M-mode image of pleural effusion.